
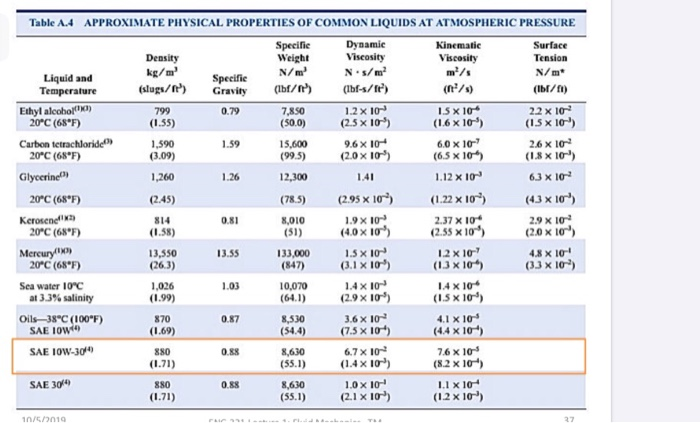
Only informative sections of standards are publicly … WebThe table below gives some examples of fluids together with their dynamic and kinematic viscosities.

#WATER VISCOSITY CALCULATOR FREE#
Temperature and Pressure - Free online calculator - figures and tables with viscosity of water at temperatures ranging 0 to 360☌ (32 to 675☏) - … Web20 de jan. Water - Dynamic (Absolute) and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure - Absolute viscosity for water in centipoises for temperatures between 32 - 200 o F. The 3d structure may be viewed using Java or … Viscosity - Wikipedia Viscosity of liquid water in the range −8 ☌ to - NIST Viscosity of Liquids and Gases - HyperPhysics WebWater - Absolute (Dynamic) Viscosity vs. Chemical structure: This structure is also available as a 2d Mol file or as a computed 3d SD file. Temperature … Viscosity of Water – viscosity table and viscosity chart - Anton Paar Viscosity - Wikipedia WebCAS Registry Number. t – temperature p – pressure ρ – density cp – specific heat μ – dynamic viscosity ν – kinematic viscosity offbeat hidden gem Viscosities of Common Fluids - Oil Viscosity Chart Water - Absolute (Dynamic) Viscosity vs. For temperatures higher than 100 O C, values are for water at boiling conditions. Table B-1 is presented information at regular intervals of temperature while Table B-2 is presented at … Water - Density Viscosity Specific Weight - Engineers Edge WebThis table gives values of water properties – density, viscosity and specific heat in relation to temperature. A poise (P), named after Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille, who also derived the Poiseuille's law equation, has a value equivalent to 0.1 pascals-second (Pa⋅s).Water viscosity table Water Viscosity Calculator - Find Dynamic & Kinematic Viscosity Liquid viscosity : chart of 150+ common liquids - WebTables B-1 and B-2 present data for saturated liquid and saturated vapor. Now that we know the difference between the two types of viscosities, let's go back to the measurement units. By determining the viscosity of fuels in terms of kinematic viscosity, we get to model the speed fuel droplets that will be sprayed out of an injection nozzle due to applied pressure. One particular use of kinematic viscosity is for fuels. On the other hand, we use kinematic viscosity to describe the speed of the fluid due to an applied force. Learn more about squeezing pressure on a container with fluids by checking out our manometer calculator. That way, it won't be either too hard to squeeze the paste out of the tube or too runny that a lot of paste comes out, even with a little squeezing pressure.
When formulating the mixture of, let's say, a paste in a tube, we want the paste to have a specific dynamic viscosity. The dynamic viscosity tells us how much force is required for a fluid to move at a particular speed. Viscosity, which describes a fluid's consistency or "thickness," comes in these two types for some distinct reasons.

Poise is a unit of measurement used particularly for dynamic viscosity, while stokes is for kinematic viscosity. Poise and stokes are units of measure used to quantify viscosity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
